Introduction
Chemical compounds play a crucial role in various industries, research fields, and even in the origins of life. Two such compounds, HCOOCH (Methyl Formate) and CH₂H₂O (Glycolaldehyde) have significant importance in organic chemistry, astrophysics, and industrial applications. In this article, we will explore the properties, synthesis, applications, and scientific significance of these two molecules.
HCOOCH (Methyl Formate): An Overview
Chemical Structure and Properties
Methyl formate (HCOOCH) is an organic ester derived from formic acid and methanol. It has the following characteristics:
- Molecular Formula: HCOOCH₃
- Molecular Weight: 60.05 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Odor: Sweet, similar to rum
- Boiling Point: 31.5°C
- Density: 0.97 g/cm³
- Solubility: Soluble in water and organic solvents
Methyl formate is known for its volatile nature and pleasant odor, making it useful in various industrial applications.
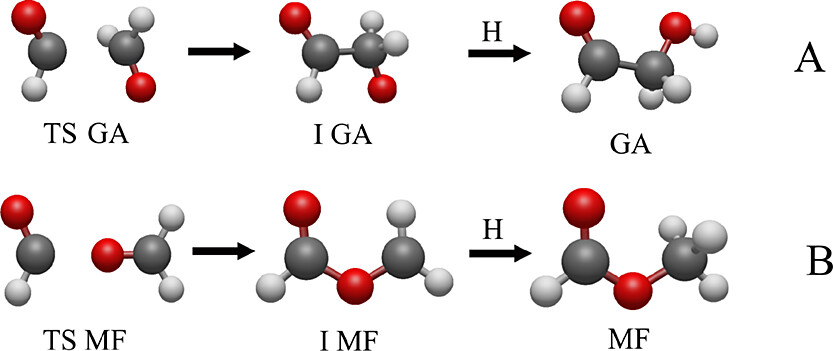
Synthesis of Methyl Formate
Methyl formate is commonly synthesized using the esterification process, where formic acid reacts with methanol in the presence of a catalyst like sulfuric acid:
Alternatively, it can be produced industrially through the catalytic carbonylation of methanol with carbon monoxide.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
Methyl formate has multiple industrial uses, including:
- Solvent in Chemical Synthesis: Used in the production of formamides and other organic compounds.
- Foam Blowing Agent: Employed in the manufacture of polyurethane foams.
- Insecticide and Pesticide Manufacturing: Acts as an intermediate in agricultural formulations.
- Fragrance and Flavoring Agent: Used in food and perfume industries for its sweet, fruity scent.
- Fuel Additive: Enhances combustion efficiency in specific fuel mixtures.
Role in Astrophysics and Space Chemistry
Methyl formate has been detected in interstellar space, particularly in star-forming regions like Sagittarius B2. This discovery suggests the presence of complex organic molecules in space, supporting theories about the extraterrestrial origin of life’s building blocks.
CH₂H₂O (Glycolaldehyde): An Overview
Chemical Structure and Properties
Glycolaldehyde (CH₂H₂O) is the simplest sugar-related molecule, classified as an aldehyde. Its properties include:
- Molecular Formula: C₂H₄O₂ (commonly simplified as CH₂H₂O)
- Molecular Weight: 60.05 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless solid or liquid
- Melting Point: 20°C
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water
- Reactivity: Can undergo polymerization and oxidation reactions
Glycolaldehyde is of great interest in both organic chemistry and astrobiology due to its role as a precursor to more complex carbohydrates.
Synthesis of Glycolaldehyde
Glycolaldehyde can be synthesized using various methods, including:
- Oxidation of Ethylene Glycol:
- Formose Reaction: A self-catalytic process where formaldehyde polymerizes under basic conditions to form glycolaldehyde and other sugars.
- Laboratory Synthesis: Using formaldehyde or sugar hydrolysis processes.
Biological and Industrial Applications
Glycolaldehyde is important in several fields:
- Prebiotic Chemistry: A potential precursor to ribose, a fundamental sugar in RNA.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Plays a role in caramelization and Maillard reactions, influencing flavor and aroma in baked goods.
- Pharmaceutical Research: Used in studies related to metabolic pathways and enzyme reactions.
- Polymer Chemistry: Serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
Glycolaldehyde in Space and the Origins of Life
The presence of glycolaldehyde in space, particularly in star-forming regions, has been confirmed through radio astronomy. It is significant because it provides evidence that essential biological molecules can form in space and may have contributed to the development of life on Earth through meteorite impacts.
Comparative Analysis of HCOOCH and CH₂H₂O
| Property | HCOOCH (Methyl Formate) | CH₂H₂O (Glycolaldehyde) |
| Molecular Formula | HCOOCH₃ | C₂H₄O₂ |
| Molecular Weight | 60.05 g/mol | 60.05 g/mol |
| State | Liquid | Solid/Liquid |
| Solubility | Soluble in water and organic solvents | Highly soluble in water |
| Industrial Use | Solvent, fuel additive, pesticide, foam production | Pharmaceutical, food industry, polymer chemistry |
| Astrobiological Significance | Detected in space, precursor to organic molecules | Found in interstellar space, precursor to sugars |
Conclusion
Both methyl formate (HCOOCH) and glycolaldehyde (CH₂H₂O) are fascinating molecules with significant industrial, chemical, and astrophysical implications. Methyl formate is widely used in various industries, while glycolaldehyde is crucial in prebiotic chemistry and biological research. Their discovery in space further reinforces the theory that complex organic molecules could have originated beyond Earth, potentially playing a role in the emergence of life.
Understanding these molecules not only enhances our knowledge of organic chemistry but also provides valuable insights into the fundamental processes that govern life and the universe.